MC A relation is in 3 NF if it satisfies 2 NF and... no primary key of R is transitively dependent on a prime attribute type. incorrect no prime attribute type of R is transitively dependent on the primary key. incorrect no non-primary key of R is transitively dependent on a prime attribute type. incorrect no nonprime attribute type of R is transitively dependent on the primary key. correct
MC Which statement is CORRECT? A foreign key of a relation A cannot refer to the primary key of the same relation A. incorrect Every relation must have a foreign key. incorrect A relation cannot have more than 1 foreign key. incorrect A foreign key can be NULL. correct
MC Given the following relational model (primary keys are underlined, foreign keys in italics):
STUDENT(studentnumber, studentname, street name, street number, zip code, city)
ENROLLED(student_number, course_number)
COURSE(course number, course name)
PROFESSOR(professor number, professor name)
TEACHES(course number, professor number)
Which statement is CORRECT? The model can be further normalized. correct The model does not allow a professor to teach multiple courses. incorrect The model does not allow a course to be taught by multiple professors. incorrect The model does not allow a course to be followed by multiple students. incorrect
MC Given the following (normalized) relational model (primary keys are underlined, foreign keys are in italics).
EMPLOYEE(SSN, ENAME, EADDRESS, SEX, DATE_OF_BIRTH, SUPERVISOR, DNR)
SUPERVISOR: foreign key, refers to SSN in EMPLOYEE, NULL value allowed
DNR: foreign key, refers to DNR in DEPARTMENT, NULL value not allowed
DEPARTMENT(DNR, DNAME, DLOCATION, MGNR)
MGNR: foreign key, refers to SSN in EMPLOYEE, NULL value not allowed
PROJECT(PNR, PNAME, PDURATION, DNR)
DNR: foreign key, refers to DNR in DEPARTMENT, NULL value not allowed)
WORKS_ON(SSN, PNR,, HOURS)
SSN: foreign key, refers to SSN in EMPLOYEE, NULL value not allowed
PNR: foreign key, refers to PNR in PROJECT, NULL value not allowed
Which statement is CORRECT? According to the model, an employee should always work on projects assigned to his/her department. incorrect According to the model, a supervisor cannot supervise more than one employee. incorrect According to the model, an employee can manage multiple departments. correct According to the model, an employee can work in multiple departments. incorrect
MC The following relational model represents a HRM system of a consultancy firm. The primary keys are underlined while foreign keys are in italic font.
Consultant (ConsultantID, Date of Birth, Expertise)
Assigned_to (ConsultantID, ProjectID)
ConsultantID refers to ConsultantID in Consultant
ProjectID refers to ProjectID in Project
Project (ProjectID, Description, Type, Company)
Company refers to Name in Company
Company (Name, Location)
Suppose a new consultant is hired and immediately assigned to a new training project at a new firm and to 2 other, already existing projects. How many rows (tuples) must be added to the database to reflect this change? 5 incorrect 1 incorrect 6 correct 3 incorrect
MC Given the following (normalized) relational model (primary keys underlined; foreign keys in italics):
EMPLOYEE(SSN, ENAME, EADDRESS, SEX, DATE_OF_BIRTH, SUPERVISOR, DNR)
SUPERVISOR: foreign key, refers to SSN in EMPLOYEE, NULL value not allowed
DNR: foreign key, refers to DNR in DEPARTMENT, NULL value not allowed
DEPARTMENT(DNR, DNAME, DLOCATION, MGNR)
MGNR: foreign key, refers to SSN in EMPLOYEE, NULL value not allowed
PROJECT(PNR, PNAME, PDURATION, DNR)
DNR: foreign key, refers to DNR in DEPARTMENT, NULL value not allowed
WORKS_ON(SSN, PNR, HOURS)
SSN: foreign key, refers to SSN in EMPLOYEE, NULL value not allowed
PNR: foreign key, refers to PNR in PROJECT, NULL value not allowed
Which statement is NOT CORRECT? A department has always exactly one manager. incorrect Every project is always assigned to exactly one department. incorrect An employee must work in the same department than he/she manages. correct Every employee must be always supervised by exactly one other employee. incorrect
MC Given the following relational model (primary keys are underlined, foreign keys are in italics)
BOOK(ISBN, title, pages, price, publishername)
AUTHOR(authorname, date_of_birth)
WRITES(authorname, ISBN)
PUBLISHER(publishername, streetnumber, streetname, zipcode)
CITY(zipcode, city)
The assumptions are: - Each book has a unique ISBN number
- Each author has a unique name
- Each publisher has a unique name
- A book can have multiple authors
- An auther can write more than one book
- A publisher can publish more than one book
- A book can have multiple publishers
- A publisher has only one address
Which statement is CORRECT? The relational model is in first normal form but not in second normal form. incorrect The relational model is in third normal form. incorrect The relational model is not in first normal form. correct The relational model is in second normal form but not in third normal form. incorrect
MC Given the following relational model (primary keys are underlined, foreign keys are in italics)
BOOK(ISBN, title, pages, price, publishername)
AUTHOR(authorname, date_of_birth)
WRITES(authorname, ISBN)
PUBLISHER(publishername, streetnumber, streetname, zipcode)
CITY(zipcode, city)
The assumptions are: - Each book has a unique ISBN number
- Each author has a unique name
- Each publisher has a unique name
- A book can have multiple authors
- An auther can write more than one book
- A publisher can publish more than one book
- A book can have multiple publishers
- A publisher has only one address
Which statement is CORRECT? The relational model is in third normal form. incorrect The relational model is not in first normal form. correct The relational model is in first normal form but not in second normal form. incorrect The relational model is in second normal form but not in third normal form. incorrect
MC Consider the following ER model for a course administration.
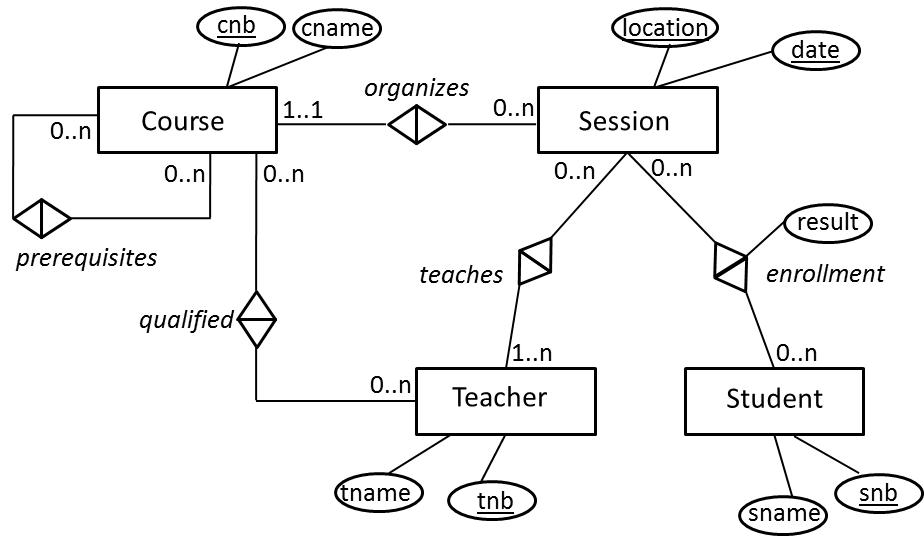
Which statement is NOT CORRECT? When mapping the ER relationship type teaches between Session and Teacher to the relational model, a new relation needs to be introduced. The 4 cardinalities of this ER relationship type can be perfectly mapped to the relational model. correct Both the ER and the relational model cannot enforce that a teacher can only teach sessions of courses for which he/she is qualified. incorrect When mapping the ER relationship type organizes between Course and Session to the relational model, the primary key "cnb" of the Course relation will be included as a NOT NULL foreign key in the Session relation. The 4 cardinalities of this ER relationship type can be perfectly mapped to the relational model. incorrect When mapping the ER relationship type enrollment between Session and Student to the relational model, a new relation needs to be introduced. The 4 cardinalities of this ER relationship type can be perfectly mapped to the relational model. incorrect
MC Consider following generalization / specialization.
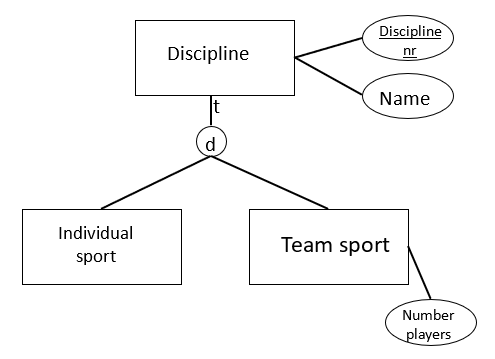
Suppose we represent this generalization / specialization by the following relational model:
Discipline (Disciplinenr, Name)
Individual sport (Disciplinenr) Disciplinenr refers to Disciplinenr in Discipline
Teamsport (Disciplinenr, Number players) Disciplinenr refers to Disciplinenr in Discipline
Consider the following 4 statements:
1) The relational model does not allow to enforce the completeness constraint; the disjointness constraint can be enforced.
2) The relational model does not allow to enforce both the completeness constraint and the disjointness constraint.
3) By dropping the relation 'Discipline' in the relational model, the completeness constraint can be enforced.
4) The relational model allows the specialization to be partial.
Which of the following options is CORRECT? Only statement 1 is incorrect, the other statements are correct. correct Only statement 4 is incorrect, the other statements are correct. incorrect Statement 1 and 2 are both correct. incorrect Statement 1 and 4 are both incorrect. incorrect

